Essential amino acids (EAAs) are the building blocks of life and play a crucial role in your health, muscle growth, and metabolic functions. These amino acids are indispensable because your body cannot produce them on its own and therefore they must be obtained through diet. In this article, you will learn everything you need to know about essential amino acids, their importance, and how to ensure you get enough of them.
Essential amino acids are not only important for athletes and fitness enthusiasts but for everyone who wants to improve their overall health and well-being. They are involved in a variety of bodily functions, from muscle repair to supporting the immune system. A deficiency in these important nutrients can lead to various health problems, so it is important to ensure you have enough of them in your diet or through Nutraceuticals supplemented.
What are essential amino acids?
Essential amino acids are organic compounds your body needs to synthesize proteins. Unlike non-essential amino acids, which your body can produce itself, essential amino acids must be obtained through diet. There are nine essential amino acids that are vital for various bodily functions. These are leucine, isoleucine, valine, tryptophan, phenylalanine, threonine, methionine, lysine, and histidine.
The human body requires a total of 20 different amino acids to form proteins. Eleven of these can be synthesized by the body itself, while the remaining nine, the essential amino acids, must be obtained through food. These nine amino acids are so important because they are essential for the growth, repair, and maintenance of body tissues.
Why essential amino acids are indispensable
Essential amino acids significantly contribute to muscle repair, the immune system, hormone production, and mental performance. They play a central role in metabolism and are vital for overall well-being. A deficiency in essential amino acids can lead to various health problems, so it is important to regularly consume them in sufficient amounts.
Muscle repair and growth
Essential amino acids are crucial for the repair and growth of muscle tissue. They help regenerate muscles after physical exertion and contribute to muscle building. Particularly important are the branched-chain amino acids (BCAAs) leucine, isoleucine, and valine, which make up about one-third of muscle proteins.
Support of the immune system
A strong immune system is important to fend off infections and stay healthy. Essential amino acids play a key role in the production of antibodies and immune cells. They help optimize immune function and make your body more resilient against diseases.
Hormone production
Essential amino acids are involved in the production of various hormones responsible for regulating metabolism, growth, and mood. For example, tryptophan is a precursor to serotonin, a neurotransmitter that influences mood and sleep.
Mental performance
Some essential amino acids are important for brain function and mental performance. They contribute to the production of neurotransmitters responsible for communication between nerve cells. Adequate consumption of these amino acids can improve cognitive function and promote mental clarity.
The 9 essential amino acids and their functions
Leucine
Leucine is one of the three branched-chain amino acids (BCAAs) and plays a central role in muscle metabolism. It promotes protein synthesis and helps prevent muscle breakdown. Leucine is especially important for athletes and active individuals as it supports muscle regeneration and growth.
Isoleucine
Isoleucine is another BCAA that contributes to energy production and muscle repair. It helps supply muscles with energy during intense physical activities and supports recovery after training. Isoleucine is also involved in regulating blood sugar levels.
Valine
Valine, the third BCAA, is important for muscle coordination and mental well-being. It helps stabilize muscles during physical exertion and contributes to mental endurance. Valine also supports energy production and muscle repair.
Tryptophan
Tryptophan is a precursor to serotonin and melatonin, two neurotransmitters that regulate mood and sleep. It helps reduce stress and improve sleep quality. Tryptophan is also important for protein synthesis and brain function.
Phenylalanine
Phenylalanine is important for the production of neurotransmitters such as dopamine and norepinephrine, which influence mood and cognitive function. It contributes to mental alertness and concentration and supports pain relief.
Threonine
Threonine is an important component of collagen and elastin, two proteins essential for skin health and wound healing. It supports antibody production and contributes to immune function. Threonine is also important for digestion and nutrient absorption.
Methionine
Methionine is important for protein synthesis and liver health. It helps break down fats and protect the liver from damage. Methionine is also involved in the production of creatine, which supports muscle energy and performance.
Lysine
Lysine promotes collagen production and calcium absorption, which is important for the health of bones and connective tissue. It supports immune function and helps fend off viruses. Lysine is also important for protein synthesis and tissue repair.
Histidine
Histidine is important for the production of red blood cells and immune function. It helps reduce inflammation and supports tissue healing. Histidine is also involved in regulating the body's acid-base balance.
How do I take essential amino acids correctly?
To achieve the best results, essential amino acids should be taken in the right dosage and at the right time. Here are some tips:
-
Dosage: The recommended daily dose is between 10-15 grams, depending on your activity level and goals. Athletes and active people may require higher doses to meet increased needs.
-
Timing: For muscle building, it is best to take amino acids before and after training. This helps supply the muscles with the necessary building blocks for repair and growth. Taking amino acids before bedtime can also be beneficial, as the body regenerates during this time.
-
Combination: Combine EAAs with carbohydrates for better absorption. Carbohydrates promote insulin release, which in turn supports the uptake of amino acids into the muscles.
-
With or without food: EAAs can be taken with or without food, depending on personal preference and tolerance. If you are sensitive to supplements, it may be helpful to take them with meals to avoid stomach discomfort.
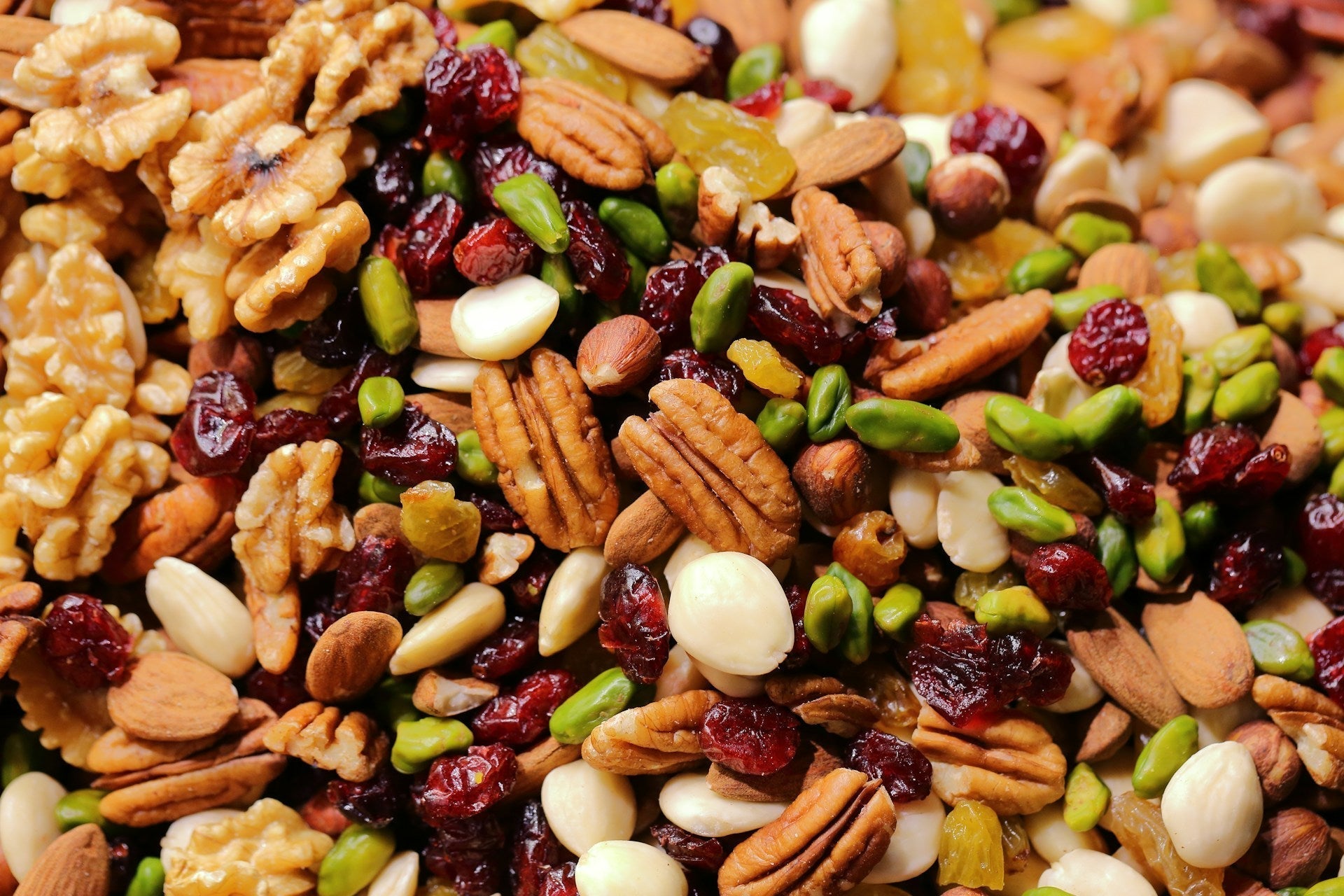
Natural sources of essential amino acids
Besides supplements, there are many natural sources of essential amino acids:
-
Animal products: Meat, fish, eggs, and dairy products are excellent sources of essential amino acids. They contain all nine EAAs in sufficient amounts and are easily digestible.
-
Plant-based products: Legumes, quinoa, nuts, and soy are good plant-based sources of essential amino acids. These foods are especially important for vegetarians and vegans who need to cover their protein intake from plant sources.
Conclusion
Essential amino acids are indispensable for your health and well-being. Through a balanced diet and, if necessary, the intake of dietary supplements you can ensure that your body is sufficiently supplied with these important building blocks.
An adequate supply of essential amino acids is crucial for maintaining muscle mass, supporting the immune system, and overall health. By paying attention to a balanced diet and using supplements if needed, you can ensure that your body functions optimally and you achieve your fitness and health goals.
Legal notice regarding health-related claims:
Our information is for general informational purposes only and does not replace medical advice. Dietary supplements do not replace a balanced diet and a healthy lifestyle. Health-related claims about dietary supplements must comply with the Health Claims Regulation (EC) No. 1924/2006 and be approved by the European Food Safety Authority (EFSA). If you have health complaints or questions, please consult a doctor.
Legal notice regarding health-related claims:
Our information is for general informational purposes only and does not replace medical advice. Dietary supplements do not replace a balanced diet and a healthy lifestyle. Health-related claims about dietary supplements must comply with the Health Claims Regulation (EC) No. 1924/2006 and be approved by the European Food Safety Authority (EFSA). If you have health complaints or questions, please consult a doctor.